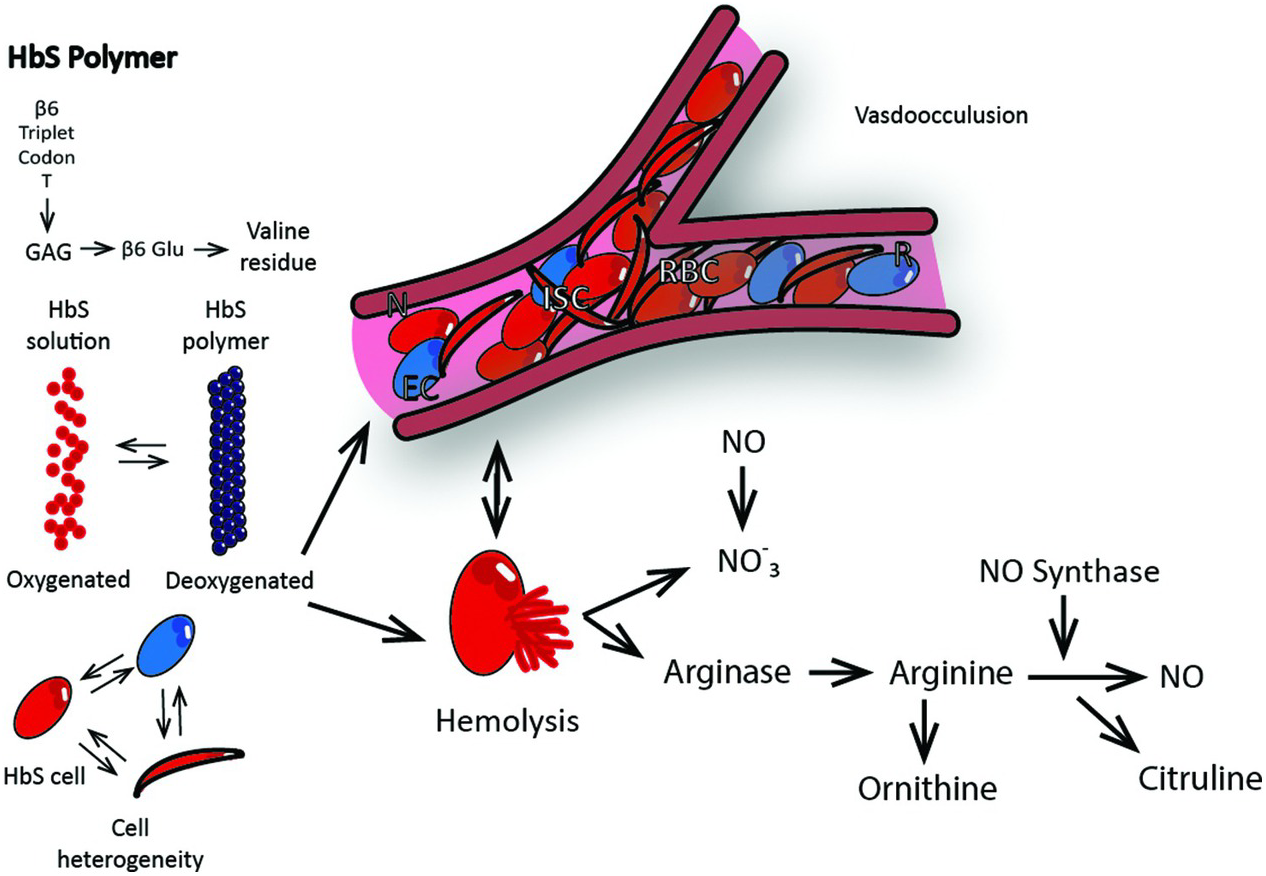
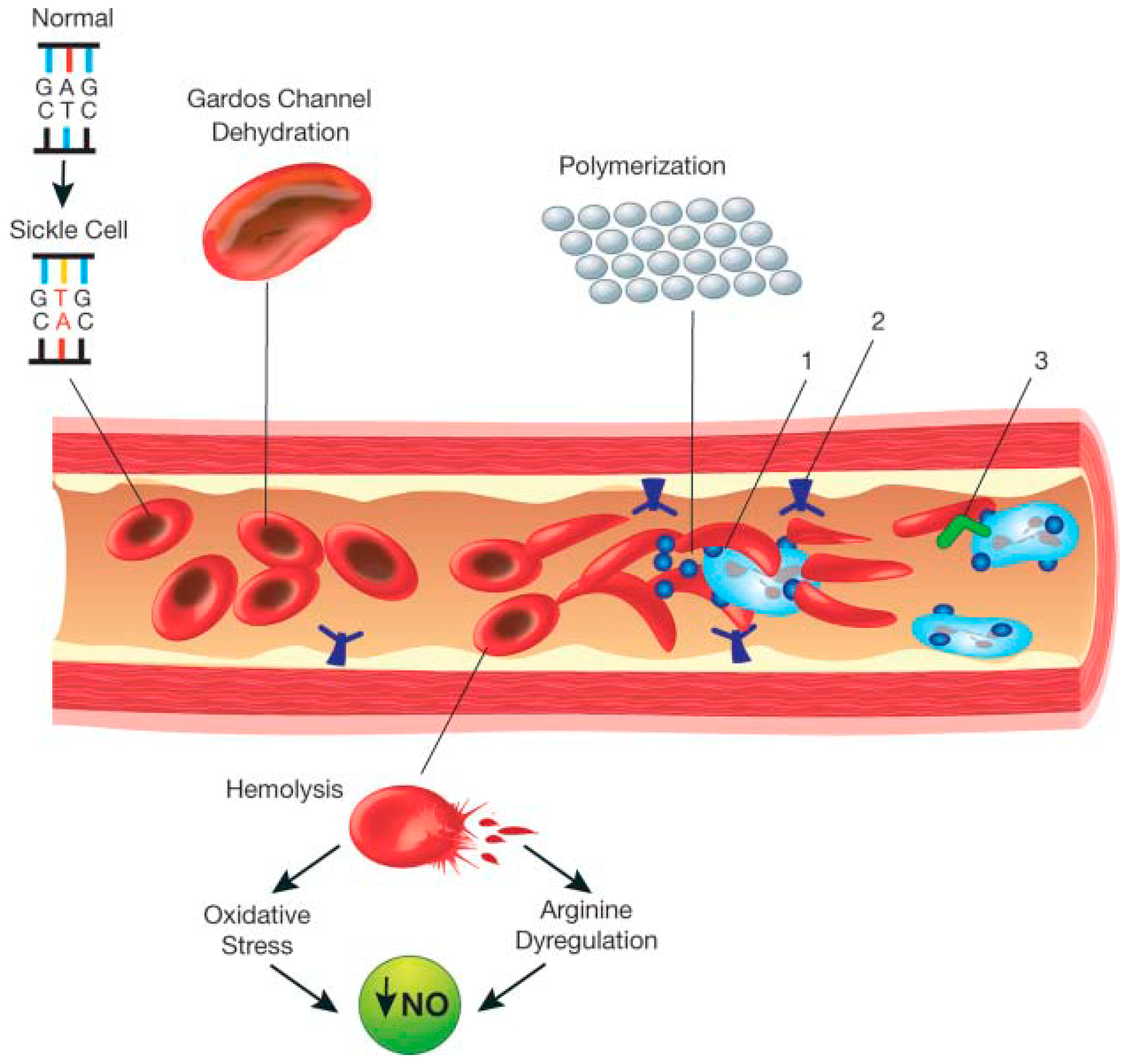
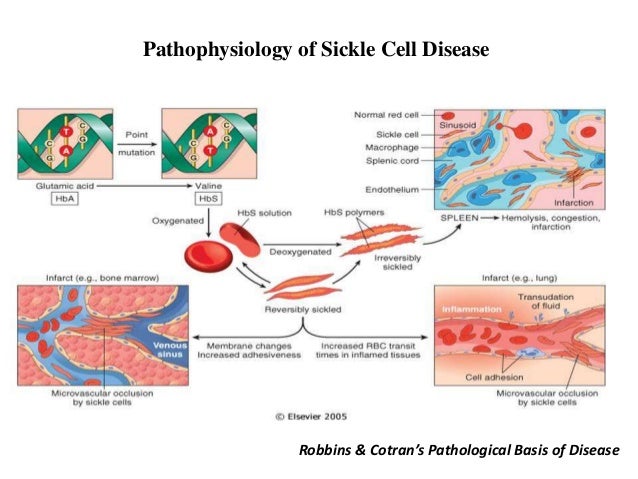
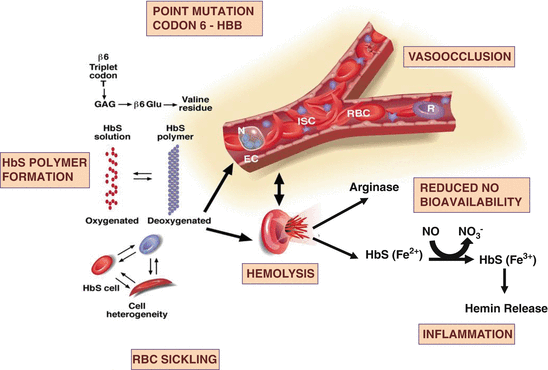
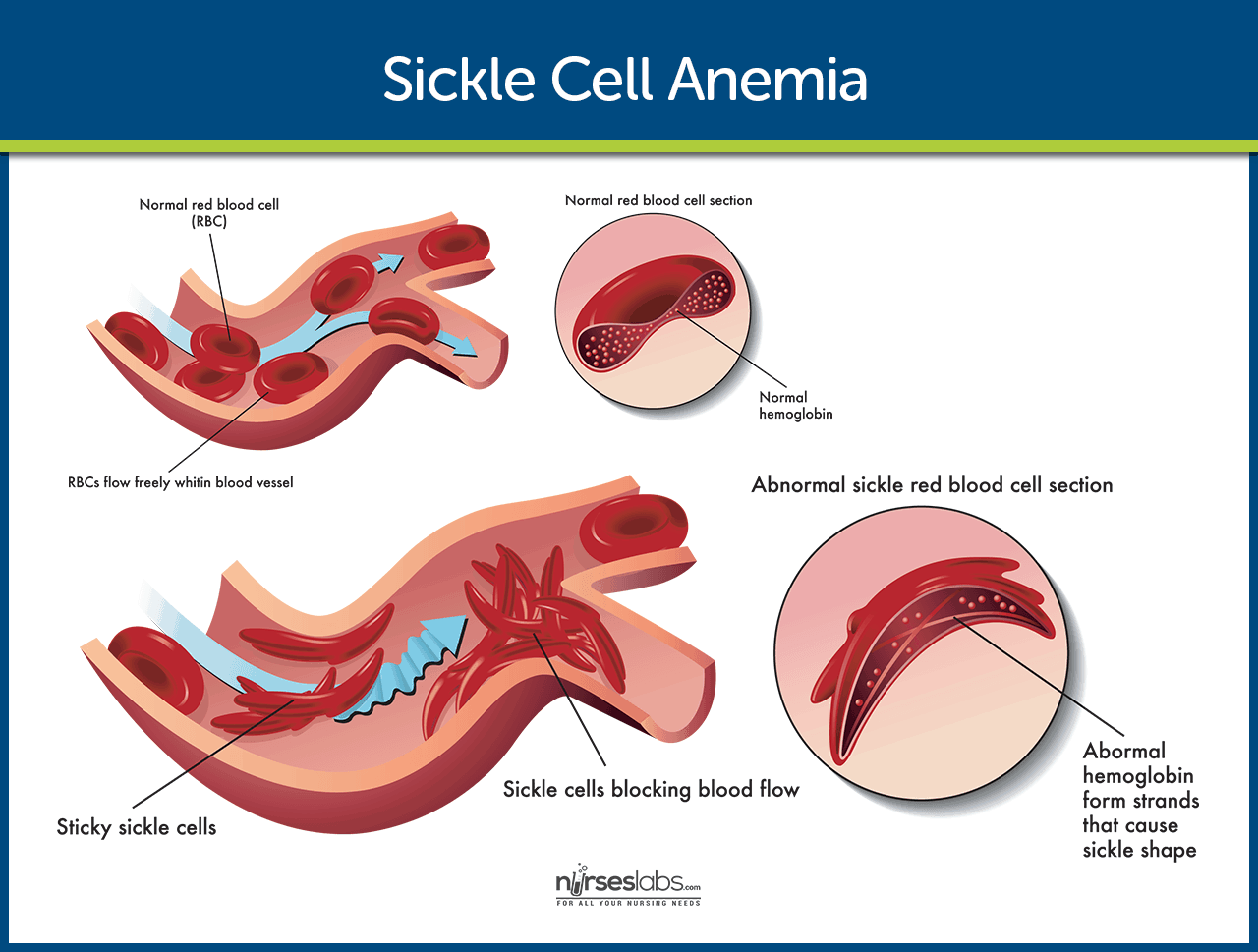
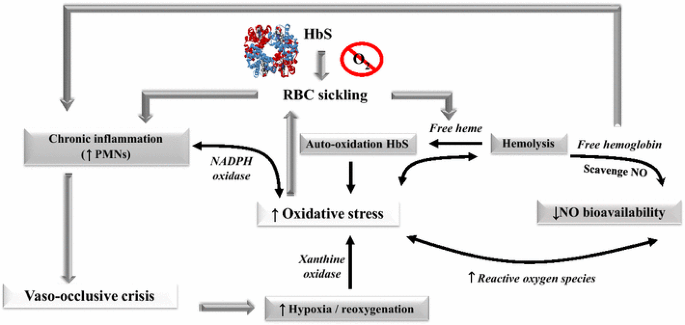
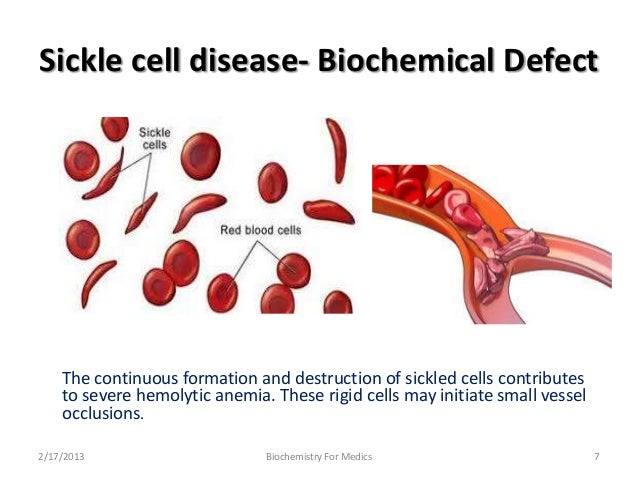
Hemolysis in sickle cell disease. Abnormal rigidity of the cells and the unusual tendency of HbSS cells to adhere to macrophages play an important role in short RBC survival. 12 In sickle cell disease hemolysis is the consequence of hemoglobin S Hb S polymerization which causes red cell rigidity and sickling. 2005 Nov 16294 192432-3.
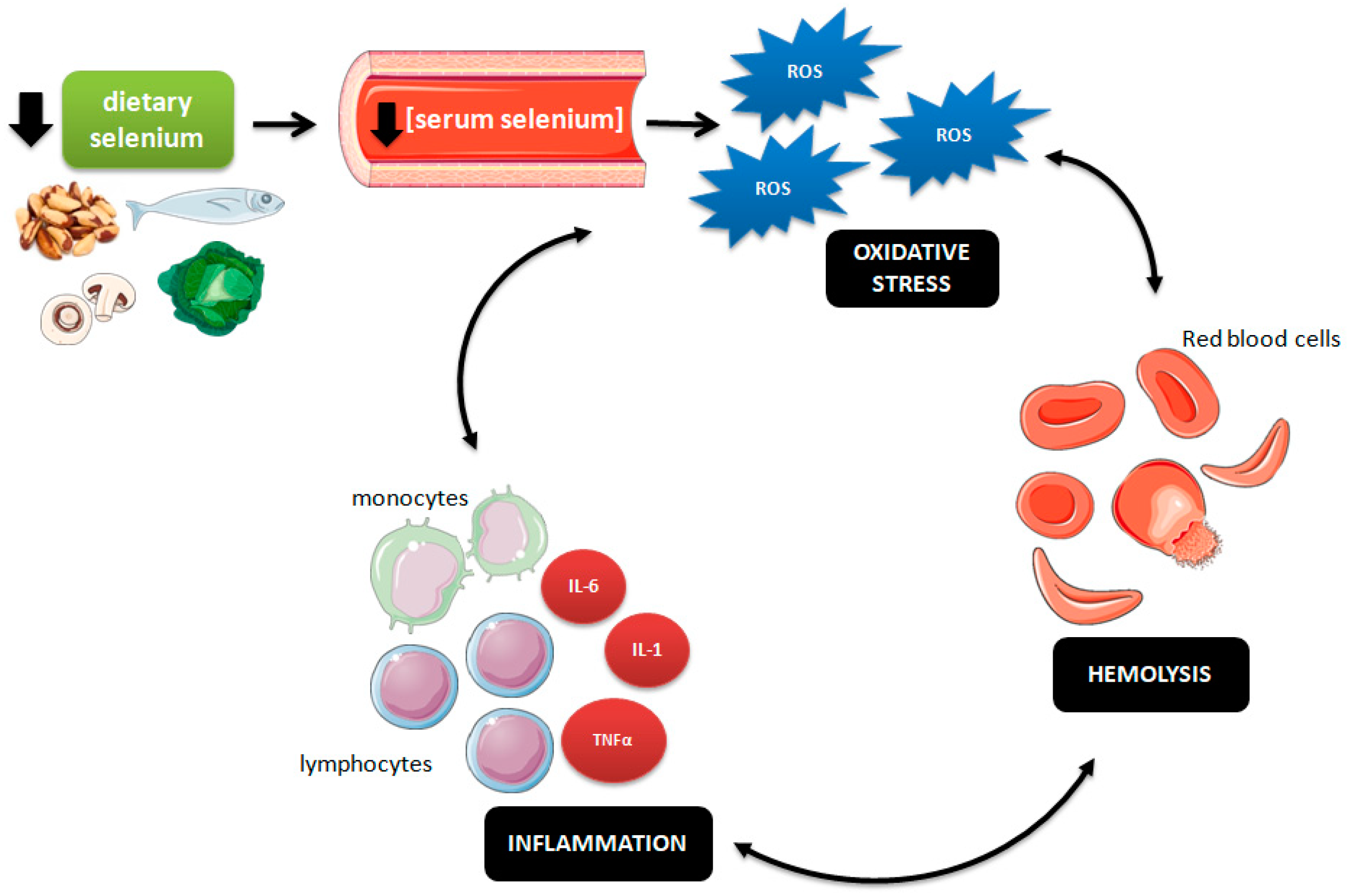
It is caused by homozygous inheritance of genes for hemoglobin Hb S. Our hypothesis was that some antioxidant micronutrients retinol tocopherol selenium and zinc would be determinant factors of the degree of hemolysis in SCD patients. Hemoglobin SS HBSS genotype is associated with most of these complications.
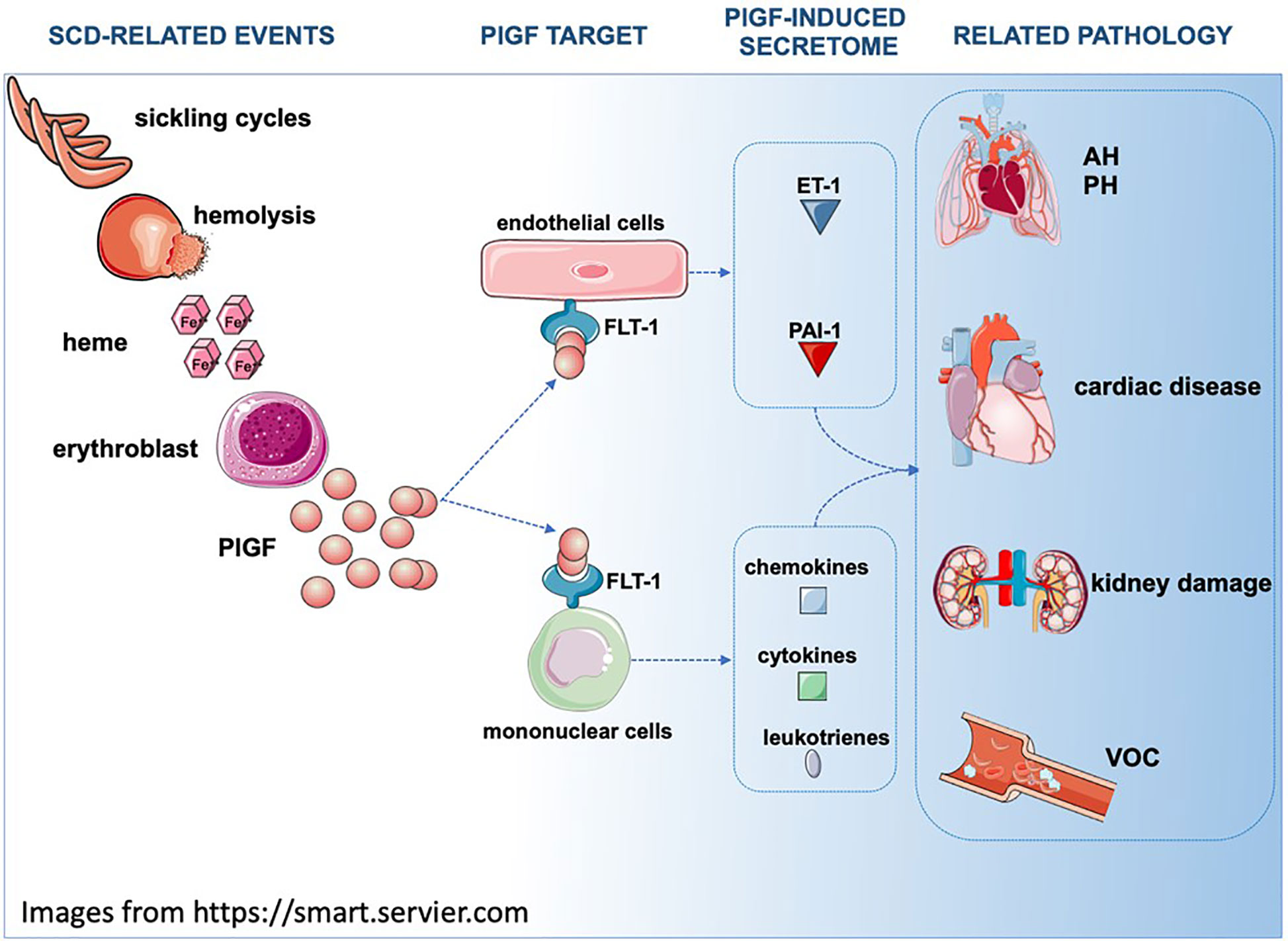
A common feature of both sickle cell disease and thalassemia is intravascular hemolysis and chronic anemia. In this context pulmonary hypertension is emerging as one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in adult sickle cell and thalassemia patients and likely in patients with other hemolytic anemias. Patients with sickle cell disease have an increased risk of priapism which has been related to chronic hemolysis.
Dysregulated arginine metabolism hemolysis-associated pulmonary hypertension and mortality in sickle cell disease. Hemolysis is the breakdown of red blood cells. Sickle cell disease SCD is an inherited hemoglobin disorder resulting in homozygous hemoglobin S.
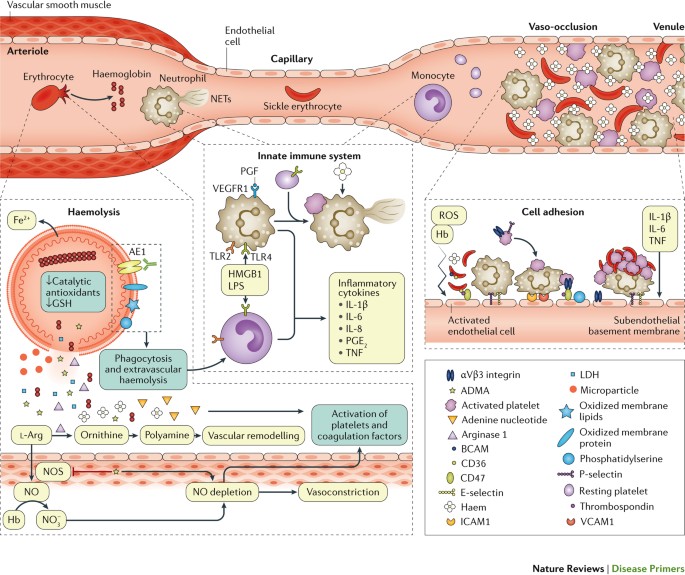
Chronic hemolysis is promoted by increased oxidative stress. Intravascular hemolysis can impair NO bioavailability and cause. This process results in fewer red blood cells.
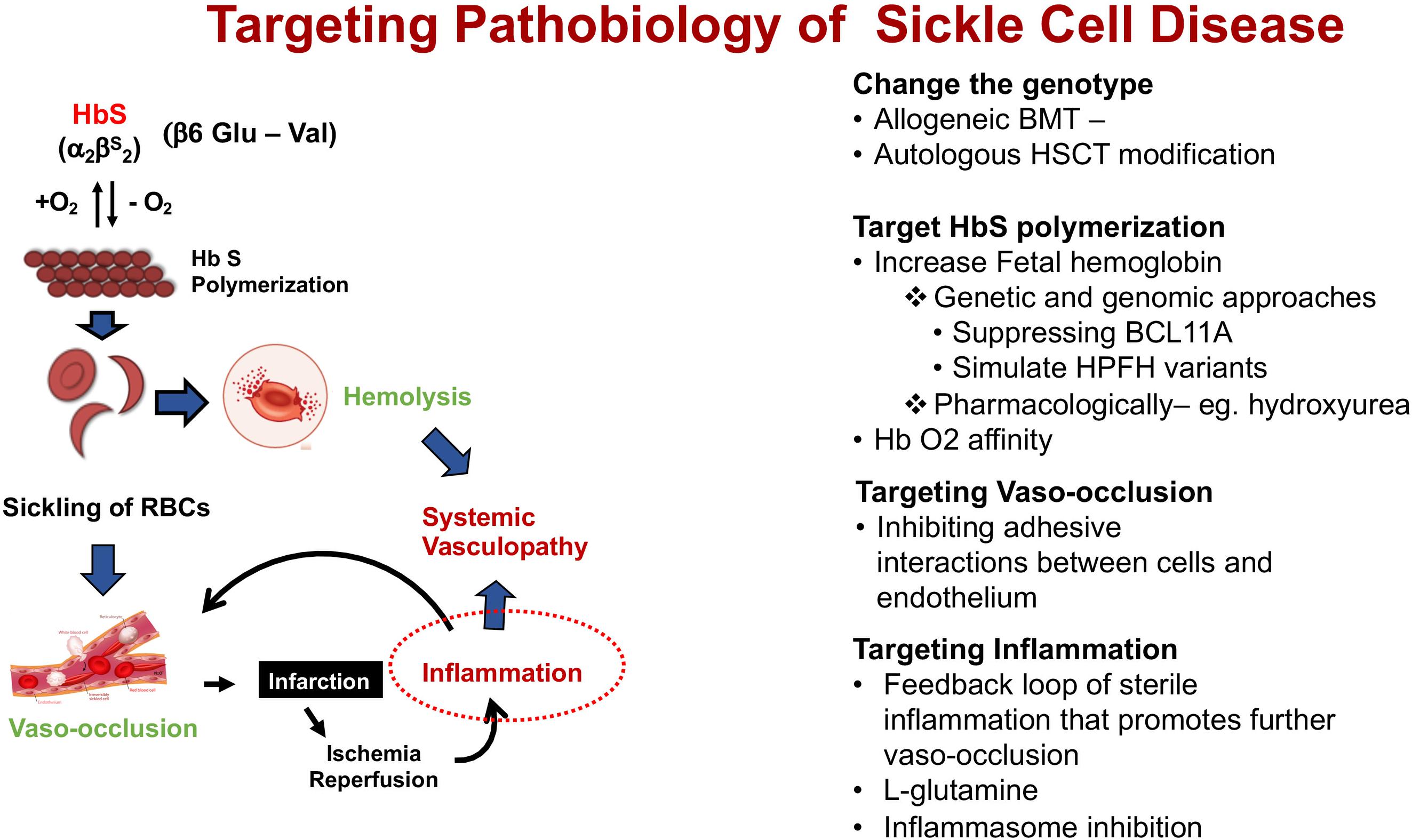
The causative mutation in the gene encoding the hemoglobin subunit β HBB leads to various genotypic variants of the disease. In sickle cell red blood cells breakdown faster than they should to be able to supply the body with all the oxygen it needs. In 958 of the subjects with sickle cell disease the ASTALT ratio was 1 but our results did not suggest overt malfunctioning of the liver and heart in the majority of subjects.
In addition to treating acute events such as sickle cell crisis transfusions can also reduce perioperative complications in SCD patients. In the subjects with sickle cell disease the increases in AST levels were far higher than for ALT supporting its release via intravascular hemolysis.
It is caused by homozygous inheritance of genes for hemoglobin Hb S.
Morris CR 1 Kato GJ Poljakovic M Wang X Blackwelder WC Sachdev V Hazen SL Vichinsky EP Morris SM Jr Gladwin MT. 2005 Nov 16294 192432-3. Sickle cell disease is characterized by intravascular and extra-vascular hemolysis and destruction of sickle cells may occur at a fairly substantial pace. In the subjects with sickle cell disease the increases in AST levels were far higher than for ALT supporting its release via intravascular hemolysis. Treatment with oral Oxbryta voxelotor leads to rapid and sustained rises in hemoglobin levels reduces red blood cell destruction hemolysis and improves overall health in adolescents and adults with sickle cell disease SCD according to full nearly 15-year data from the Phase 3. Hemolysis is a constant finding in sickle cell syndromes. A common feature of both sickle cell disease and thalassemia is intravascular hemolysis and chronic anemia. Sickle cell disease a hemoglobinopathy causes a chronic hemolytic anemia occurring almost exclusively in blacks. Sickle cell disease SCD is commonly encountered in Africa and Middle Eastern countries.
Approximately one third of RBCs undergo intravascular hemolysis possibly due to. A common feature of both sickle cell disease and thalassemia is intravascular hemolysis and chronic anemia. Intravascular hemolysis can impair NO bioavailability and cause. Morris CR 1 Kato GJ Poljakovic M Wang X Blackwelder WC Sachdev V Hazen SL Vichinsky EP Morris SM Jr Gladwin MT. Hemolysis is a constant finding in sickle cell syndromes. 12 In sickle cell disease hemolysis is the consequence of hemoglobin S Hb S polymerization which causes red cell rigidity and sickling. In addition to treating acute events such as sickle cell crisis transfusions can also reduce perioperative complications in SCD patients.


































![[English] Remember Tomorrow: Demands vs. tools provided. The setup](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh-oqoUOTcm6y7N3QIHypJfFISwphApGIJVLofPindXytZnJ0_XLoVzumqQHmwlZUALYE4s9rV20-JE8gOGeQNGW19tVN9xivlpPPYzqf-eDT8mHsfhZVFtAoWSjLIRsAciXsTMuc32LNY/w100/yasmin1.png)

0 Yorumlar